What HR features does Shiftbase offer?
Shiftbase centralises HR tasks (tracking absences, handling plus/minus hours, and managing employee documents) all within a single platform.
Ready to streamline your HR? Try it for free.
Would you like to view this website in another language?
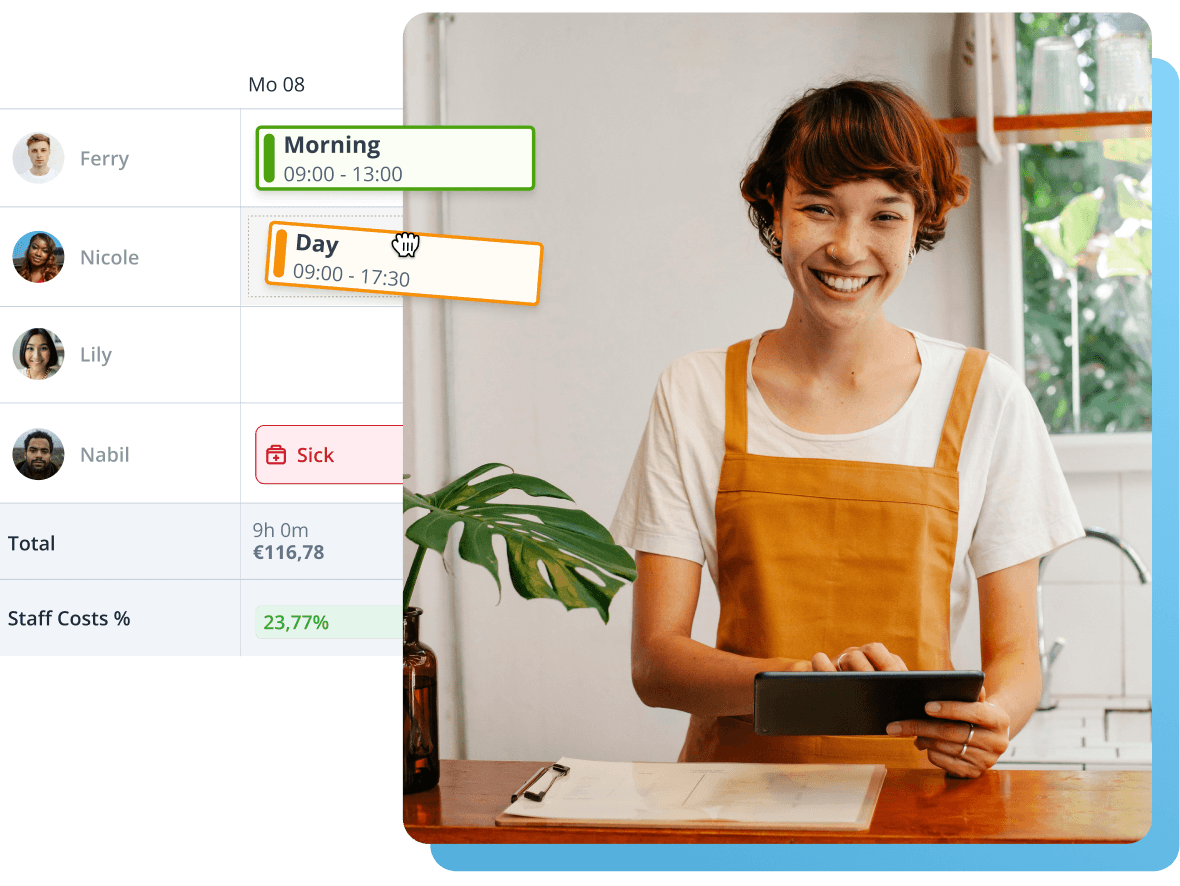
Manage absences, plus/minus-hours, and employee documents in your HRM
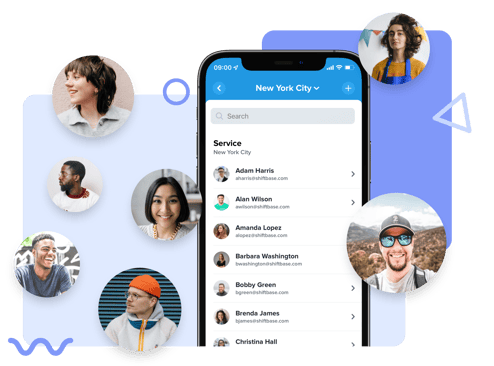
All employee data in one central place
Build a personnel file with employee notes
Automatic leave accrual
Automatic contract reminders
Notifications of anniversaries and birthdays
Automatic calculation of plus/minus-hours
Automate your personnel administration and simplify your HR processes
Improve your internal communication and keep employees informed about developments
Receive alerts when documents expire and comply with regulations
Manage your employees' competencies and certificates
Track your employees' developments in their file
Monitor your employees' well-being by tracking overtime and absences
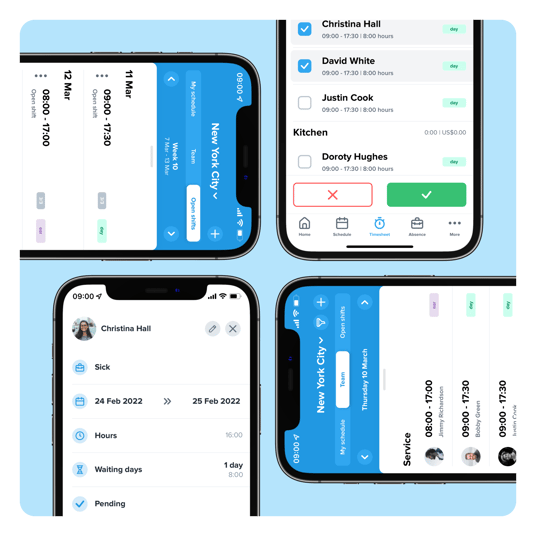
Exactly as you're used to, but from your mobile
With the HRM app, you can use all functionalities of Shiftbase
Schedule and manage shifts
Invite employees for open shifts
Register and manage worked hours
Submit and approve leave requests
ATW check
Skills
Budget & costs
Overtime allowance
Break rules
PP calculation
Managing leave types
Leave accrual
Absence policy
For more control on employee costs & happy employees, all in one platform.
4.4 of 5

4.5 of 5

4 of 5









“We are happy with Shiftbase because all our employees can easily view the schedule and indicate their availability in the app! And the customer service is helpful and responds quickly to all our questions.”
Sabrina BartenHR-employee at Flying Tiger Copenhagen
Try 14 days for free.
Our clients, big and small, come from different industries. Discover how our software can help you with your goals.
More industriesCan't find the answer to your questions here? We're happy to help you further.
Contact usShiftbase centralises HR tasks (tracking absences, handling plus/minus hours, and managing employee documents) all within a single platform.
Ready to streamline your HR? Try it for free.
Absolutely — the HRM module integrates seamlessly with employee scheduling, time tracking, and absence management features. Everything syncs in one place.
Explore integration in an interactive demo.
HR+ automates hiring admin; letting you collect new hire info, generate contracts from templates, track onboarding progress, and move hires into scheduling, all in one workflow.
During early access, HR+ is available at no extra cost for selected Basic, Premium, and Enterprise users.
Check if your plan qualifies—contact our team.
Yes — Shiftbase’s Marketplace includes dedicated HRM integrations, enabling connections with payroll, POS, and HR systems.
Browse integrations or connect yours today.
Yes — HR+ gives you a dashboard view of new hires, showing which documents are submitted, which are pending, and what remains to finalise onboarding.
Speed up your onboarding—ask for a walkthrough.
The core HRM features (like document management, absence overview, and plus/minus hours) are available immediately when you try Shiftbase (both free and paid tiers). HR+ is coming soon as an enhanced, streamlined offering.
Start your free trial today to explore what’s available now.



Scheduling that makes sense. Time tracking that just works. 100% designed for deskless teams.
No credit card needed. Cancel anytime.