In this article, we’ll explore the concept of Boolean search, illustrating its basic and proximity operators and their practical uses. Learn through LinkedIn examples, evaluate its advantages and disadvantages, and absorb tips for executing effective Boolean searches.
What is a Boolean search?
Boolean search is a type of search that uses operators to refine search results. This type of search is based on Boolean logic, developed by the British mathematician George Boole in the mid-19th century. Boolean logic is a system of mathematics that uses logical operators to determine the truth of statements. In Boolean logic, statements can only be true or false, with no in-between.
Boolean operators are words or symbols that allow you to connect search terms to create a more specific and targeted search query. The three main Boolean operators are "AND," "OR," and "NOT." The Boolean search method can be used online for everything, but HR can also use it strategically when hiring. You can narrow or expand your search pool using Boolean search terms. It'll save you time scrolling through irrelevant results (CVs).
Basic Boolean operators: How to use it
 Boolean operators can be beneficial for finding useful sources, defining the relevance of your topic, and creating vital research questions, so learning how to use them effectively can save you much time. In addition, it can be a great help when doing literature or a systematic review.
Boolean operators can be beneficial for finding useful sources, defining the relevance of your topic, and creating vital research questions, so learning how to use them effectively can save you much time. In addition, it can be a great help when doing literature or a systematic review.
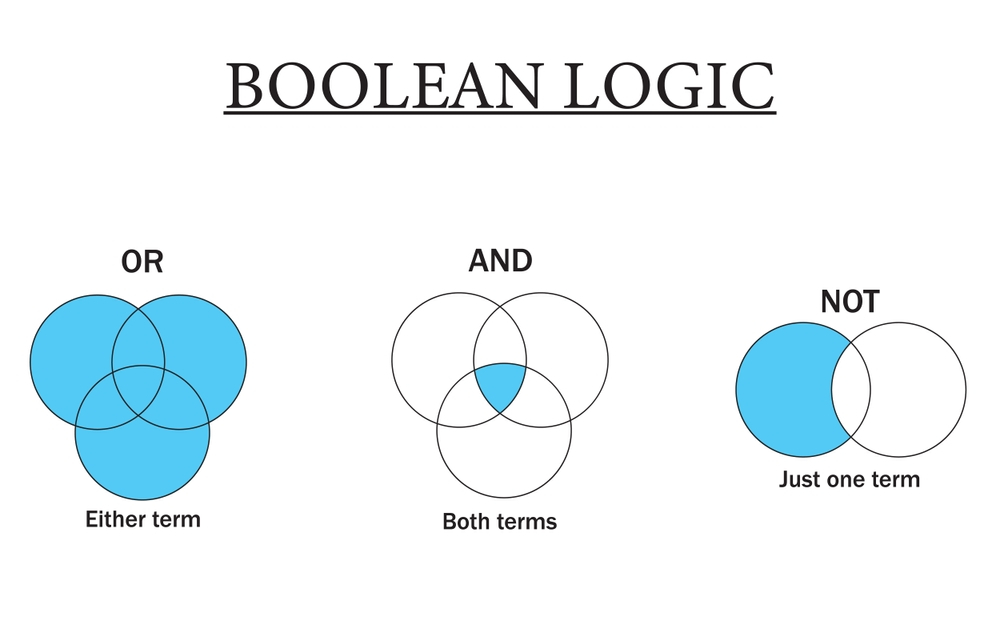
AND Boolean Operator
This operator narrow your search by finding results containing all the search terms. It can be useful if you want to get results that include two or more keywords. For example, a search for "marketing AND social media" would only return results that include both "marketing" and "social media."
OR Boolean Operator
This operator broadens the search by finding results containing at least one search term. It is useful when you want to see results that include at least one of your keywords (though not necessarily both). For example, a search for "marketing OR advertising" would return results that contain either "marketing" or "advertising" or both.
NOT Operator
This operator excludes specific words from the search. Using not will only return results related to the first keyword of your search, not the second. This can be used when you are searching for results that contain only one specific keyword. For example, a search for "marketing NOT social media" would exclude results that include the term "social media" from the search results.
Parentheses: ()
Using parentheses allows you to group keywords together and specify their order for searching, just like in a mathematical statement. Parentheses are used for keywords and Boolean operators, followed by non-parentheses for searching keywords.
The combination below, for example, will produce results that are initially filtered for "Id" or "Ego" and then further refined for "Development." As an example, use parentheses is (id OR ego) AND developmental
Parentheses can also be used more than once. The search will filter results by filtering the keywords in the innermost parentheses first, followed by those in the outer parentheses, and then by those outside parentheses.
For example, put multiple parentheses around ((id OR ego) AND Lacan) AND developmental.
Quotation marks: ""
When a quotation mark is used, search results will contain the exact keyword or two or more words contained within the quotation mark. This method is useful for finding results containing a specific keyword. In this example, the phrase "Holocene epoch" would be used in quotation marks.
Asterisk: *
An asterisk indicates that search results contain variations of the root word. It is helpful to find words that begin with the letters you entered.
Example of using an asterisk form*
The results will include variations of the chosen word, such as "formal" and "formation." Each database, search engine, or google may use a Boolean operator differently. Boolean operators are used differently in databases and search engines, so ensure you know how they work.
Many databases offer "advanced search" options, which let you choose Boolean operators from a dropdown menu, as shown below in the example from JSTOR.

Employee scheduling and Time-tracking software!
Proximity operators
The proximity operator is similar to the Boolean operator. The search engine lets you filter results based on keyword proximity. A proximity operator includes WITHIN (Wx), NEAR (Nx), and SENTENCE. Not all databases use proximity operators. Make sure you check your database's search operations.
Example LinkedIn Boolean search
The LinkedIn search engine can conduct a Boolean search for HR recruitment. Here's an example of how to search on LinkedIn using the different operators we discussed above. For example, imagine your organization is looking to hire a Team Lead in Customer Success. It will be helpful if you recruit candidates who have customer success or customer service managerial or leadership experience.
Using a Boolean search, you might find 'Customer Success' AND 'Team Leader' AND (Scale or Business). Enter your search, click 'See all results', and then 'People.' Using this search, matching profiles that contain those keywords will be displayed without job advertisements.
Pros and cons of Boolean search
Pros of Boolean search
Several search engines use boolean searches, which is one of their advantages. The ability to create booleans can enable you to navigate and take full advantage of your current applicant tracking system (ATS) or search engine. You should learn the basics of a boolean search if you want to use traditional methods of sourcing candidates.
Cons of Boolean search
The complexity of boolean searches is one of their biggest disadvantages. Even if you understand their basics, you can't expect booleans to be perfect. You can easily spend hours searching for the perfect phrase only to come up empty-handed. A small error in your search can also drastically impact the results. A boolean search isn't the most efficient way of finding new talent in an era of advanced candidate sourcing.
Tips for effective Boolean searching
While Boolean search can be a powerful tool for recruiters, it requires some knowledge and practice to be effective. Here are some tips to help recruiters create an effective Boolean string:
- Use parentheses to group related combining terms: When combining multiple search terms using operators, it's important to group related words together. It will ensure that the search engine evaluates the search string in the desired order.
- Use quotation marks for exact phrases: To search for an exact phrase, use quotation marks around the phrase. It will ensure that the search engine only returns results that include the exact phrase.
- Use wildcards for variations: Use wildcards, such as an asterisk () or a question mark (?), to capture word variations. For example, "program" will capture results for "programmer," "programming," and "programs."
- Refine search results with filters: While Boolean search can be a powerful tool, it's essential to use search filters provided by the platform to refine the search results further.
- Practice and experiment: Boolean search requires practice to master. Experiment with different operators and search strings to find the best results for your specific search criteria.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding Boolean search terms is valuable for HR professionals and recruiters who want to find qualified candidates efficiently. By using Boolean operators like AND, OR, and NOT, along with other modifiers like quotation marks and brackets, recruiters can narrow their search to find the most relevant results. With platforms like LinkedIn and other job boards, the recruitment process can be streamlined, and time can be saved to find suitable candidates. By following the tips outlined in this ultimate beginner's guide, recruiters can become Boolean search pros quickly and find the perfect candidates for their open positions.
Discover Shiftbase's Human Resources and Recruiting Blog today for an all-in-one HR solution. You will find articles on HR or recruitment, among others. Sign up for our 14 days free demo to see how Shiftbase simplifies the employee management process.
 Boolean operators can be beneficial for finding useful sources, defining the relevance of your topic, and creating vital research questions, so learning how to use them effectively can save you much time. In addition, it can be a great help when doing literature or a systematic review.
Boolean operators can be beneficial for finding useful sources, defining the relevance of your topic, and creating vital research questions, so learning how to use them effectively can save you much time. In addition, it can be a great help when doing literature or a systematic review.

